This blog contains answers to exercises set for students. While every effort is made to ensure that the information posted is correct, mistakes may occur from time to time.
Search This Blog
Monday, February 28, 2022
Markscheme for questions on Springs
1. (a) The
graph shows length and not extension of the spring / spring has
original length (of 2.0 cm) (AW)
Allow:
‘length cannot be zero’
B1
(b) Straight
line (graph) / linear graph / force µ extension / constant
gradient (graph)
Not
‘force µ length’
B1
(c) force
constant =
Note:
The mark is for any correct substitution
C1
force constant = 50 (N m–1)
Allow:
1 mark for 0.5 (N m–1) – 10n error
Allow 1 mark for 5/12 × 10–2 = 41.7 or 4/10 × 10–2 = 40 or
3/8 × 10–2 = 37.5 or 2/6 × 10–2 = 33.3 or
1/4 × 10–2 = 25
A1
(d) work
done = 1/2Fx or 1/2kx2 or ‘area under graph’
C1
work done = 1/2 × 3.0 × 0.06 or 1/2 × 50 × 0.062
Possible
ecf
work done = 0.09 (J)
Note:
1 sf answer is allowed
A1
(e) Find
the gradient / slope (of the tangent / graph)
B1
Maximum speed at 1.0s / 3.0s / 5.0s /
steepest ‘part’
of graph / displacement = 0
Allow:
2 marks for ‘steepest / maximum gradient’
B1
[8]
2. (i) It has maximum / large / increased stress
at this point
Allow:
it has ‘same force but thinner/smaller area’
Not: Thin / small area
B1
(ii) The tape has (permanent) extension /
deformation when the
force / stress is removed (AW)
Note:
Need reference to force or stress removed
Allow: ‘…does not return to original size / shape / length when force /
stress is removed’
B1
[2]
3. Copper
B1
[1]
4. extension
(or compression) ∞ force (as long as
elastic limit is not exceeded)
Allow:
‘load’ instead of force
Not: x ∞ F, unless the labels are defined
[1]
5. (i) force = 75 × 0.085
C1
F = 6.38 (N) ≈ 6.4 (N)
A1
(ii) acceleration = 6.38/2.5 x 10^-3
acceleration = 2550 (m s–2)
Note:
a = (kx-mg)/m gives 2540 (m s–2)
Possible
ecf
B1
(iii) Correct
selection of equation: mgh / 1/2x2 not equal to 1/2Fx
C1
0.0025 × 9.81 × h = 1/2 × 75 × 0.0852
C1
height = 11 (m)
Note:
Bald answer of 11 (m) scores 3/3 marks
A1
[6]
6. (a) The extension of a spring is directly
proportional to the applied force M1
as long as the elastic limit is not exceeded) A1
(b) (i) Correct
pair of values read from the graph
force constant = 12/0.080 C1
force constant = 150 (N m–1) A1
(ii) extension, x = 20/12 × 80 (= 133.33) (mm) C1
(E = ½ Fx)
energy = ½ × 2/ × 133.33 × 10–3
energy = 1.33 (J) A1
(iii) The
spring has not exceeded its elastic limit B1
(iv) (elastic potential energy = kinetic energy)
1/2 kx2 = 1/2mv2 M1
m and k are constant, therefore x µ v. M1
[9]
7. (i) Graph through origin with (short) linear
section then reducing gradient. 1
(ii) Straight section - elastic; (1)
Curved section - plastic. (1) 2
[3]
8. (a) P.E. at top = 80 × 9.8(1) × 150 = 118 000
(J) (1)
K.E. at bottom and at top = 0 (1)
Elastic P.E. at top = 0, at bottom = P.E. at top for ecf = 118 000 J (1) 3
(b) 24
N m–1 × 100 m = 2400 N 1
(c) elastic
P.E. is area under F-x graph (1)
graph is a straight line so energy is area of triangle (1)
elastic P.E. = ½ × kx × x = (½kx2) (1) 2
(d) loss
of P.E. = 100 × 9.8(1) × 150 = 147 000 J (1)
gain of elastic P.E. = ½ × 26.7 × 1052 = 147 000 J (1) 2
idea that a given (unit) extension for
a shorter rope requires a greater force 1
[9]
9. (a) One reading from the graph e.g. 1.0 N
causes 7 mm C1
Hence
5.0 (N) causes 35 ±
0.5 (mm) A1
(allow
one mark for 35 ±
1 (mm)
(b) (i) Force on each spring is 2.5 (N) C1
extension
= 17.5 (mm) allow 18 (mm) or reading from graph A1
[allow
ecf from (a)]
(ii) strain energy = area under graph / ½ F ´ e C1
= 2 ´ 0.5 ´ 2.5 ´ 17.5 ´ 10–3
= 0.044 (J) A1
[allow
ecf from (b)(i)]
[11]
10. (a) (i) F
= kx / k is the gradient of the graph C1
k
= 2.0 / 250 ´
10–3 = 8.0 A1
Correct
unit for value given in (a)(i)
i.e.
0.008 or 8 ´
10–3 requires N mm–1.
Allow
N m–1 / kg s–2 if no working in (a)(i).
Do
not allow unit mark if incorrect physics in part (a)(i) B1
(ii) W = ½
(F ´
extension) / area under the graph C1
= ½
´ 2.0 ´ 0.250
= 0.25 (J) A1
(b) (i) F = 8 ´ 0.15 = 1.2 (N) A1
(ii) Hooke’s law continues to be obeyed / graph
continues as a straight
line
/ k is constant / elastic limit has not been reached B1
(c) (i) 1. correct
time marked on the graph with a V (t = 0.75 s or 1.75 s) B1
2. tangent in the correct place for downward
velocity or implied
by values B1
value between 0.95 to 1.1(m s–1) A1
(ii) 1. X
marked in a correct place (maximum or minimum on graph) M1
2. relates the extension / compression to F
= kx to explain why the
force is a maximum or maximum
extension gives max force or
maximum extension gives max acceleration A1
[12]
Wednesday, February 23, 2022
Tuesday, February 22, 2022
Young's slits marksheme
1. (i) when
(two) waves meet/combine/interact/superpose, etc. (at a point)
M1
there is a change in overall
intensity/displacement
allow
for A1 mark: (vector) sum/resultant displacement(s)/AW
A1
(ii) constant
phase difference/relationship (between the waves)
just
stating same frequency not sufficient
B1
[3]
2. (i) path difference of nλ for
constructive interference
allow
waves arrive in phase
M1
producing either maximum
amplitude/intensity or a maximum
A1
path difference of (2n + 1)λ/2
for destructive interference
allow
waves arrive in anti-/out of phase
M1
producing either minimum
amplitude/intensity or a minimum
A1
max
3 marks; max 1 mark for two correct marking points but with n omitted
(ii) x
= λD/a = 0.030 × 5.0/0.20
C1
= 0.75 (m)
give
1 mark max for 0.75 mm but zero for 750 m
A1
(iii) 1 intensity increases by factor of 4
B1
position unchanged
B1
2 intensity unchanged
B1
distance apart of maxima is doubled
B1
3 intensity unchanged
B1
maxima move to positions of minima (and
vice versa)
B1
[11]
3. (a) (i) constant phase difference
(allow 1 mark for same phase difference or same frequency/wavelength) B2
(ii) path difference = λ/2 B1
(b) (i) evidence
shown that fringe width x = 8.0 mm B1
a = λD/x = 6.4 × 10–7 × 1.5/8.0 × 10–3 = 1.2 × 10–4 m C1
(give 2 marks for using x = 4.0 mm giving a = 2.4 × 10–4 m) A1
(ii) maximum intensity when y = 0 AND
minima at +4 and –4 B1
correct repeat distance, i.e. 8.0 mm with at least 2 full cycles drawn B1
[8]
4. (i) (wave sources have) constant phase
difference (WTTE) B1
{do
not allow “in phase” but accept “same phase difference”}
(ii) difference in length between detector and
each wave source (WTTE) B1
[2]
5. (i) 1. path
diff. = nl
(where n = 0,1,2 etc) {allow 0, OR l, OR 2l etc} B1
2. path diff = (n + ½)l (where n = 0,1,etc) {allow = 0.5l OR,1.5l, etc} B1
{do not allow answers purely about
phase diff. e.g. with degrees or
p used and
no ref to l}
(ii) recall of formula l = ax/D C1
correct
substitution for a, l
and D: e.g. ´
= (4.86 ´
10–7 ´ 2)/0.5 ´ 10–3 C1
x
= 1.94 ´
10–3 m (1.9 or 1.944) A1
(iii) central white fringe B1
other
fringes are coloured (WTTE: e.g. allow spectrum formed) B1
[7]
6. (a) (i) evidence
of good practice: i.e distance for nx measured e.g.
5x = 18mm C1
x = 3.6 mm (OR 3.5 OR 3.7) A1
{x = 3.4, 3.8, 3.9, 4.0, or 4 mm, implying ´ is directly
measured, and score 1 mark)
(ii) for O path difference = 0 B1
for
A path difference = 3(l) B1
for
B path difference = 1.5(l) B1
(b) recall
of l= ax/D
OR ´ =lD/a OR ´ µ l B1
l is smaller for
blue light (than red light) hence ´ is SMALLER (WTTE) B1
[7]
7. (i) constructive
interference/waves in phase for maxima
OR
destructive interference/waves ‘out of phase’ C1
maxima
produced when path difference is 0 OR nl (WTTE) A1
minima
produced when path difference is (n+1/2) l
(WTTE) A1
NB answers that do not account for
SERIES of both maxima and
minima can score maximum of 2 marks only)
(ii) recall of x = lD/a C1
{expressed in any form; allow unusual
symbols if correctly identified}
correct substitution: x = (3.0 ´ 50)/6 A1
x = 25 cm A1
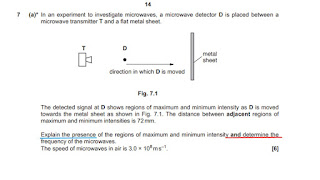
(iii) microwaves vibrate/oscillate/displaced
in one plane (WTTE) B1
{do
not allow travel/propagate in one plane)
signal
decreases to zero (WTTE) B1
[8]